Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) is a primary emergency response technique that can save lives by preserving brain function and restoring blood circulation when someone suffers from sudden cardiac arrest or another life-threatening incident. The ability to perform CPR effectively is crucial in maximizing the chances of survival for the victim, making it an essential skill not only for medical professionals but also for the general public. At Rapid CPR Dallas, we believe that accessible, comprehensive, and engaging CPR training is the key to creating a safer community where everyone can play a role in saving lives.
In this blog post, we will cover the fundamental principles of CPR, providing step-by-step guidance on performing the skill effectively. We will discuss the importance of assessing the situation and ensuring scene safety, recognizing sudden cardiac arrest, activating the emergency response system, and delivering high-quality chest compressions, rescue breaths, and, if needed, using an Automated External Defibrillator (AED).
By mastering the basics of CPR, you can make a significant difference in life-threatening situations and improve the chances of survival for individuals experiencing sudden cardiac arrest or other critical emergencies. In addition, becoming proficient in CPR training enhances personal confidence and knowledge, encouraging individuals to act promptly and effectively when faced with such situations.
1. Assessing the Situation and Ensuring Scene Safety
Before initiating CPR, it’s vital to ensure that the scene is safe. Approach the individual while checking for any hazards, such as electrical wires, chemical spills, or other dangers that may pose a threat. If the area is unsafe, call for help and wait for professional assistance rather than risking your own safety.
Once you have confirmed the scene is safe, check for responsiveness by tapping the individual’s shoulder and asking loudly if they’re okay. If they remain unresponsive, proceed to the next step.
2. Recognizing Sudden Cardiac Arrest and Activating the Emergency Response System
Sudden cardiac arrest is a serious, life-threatening event where the heart unexpectedly stops beating, causing a lack of circulation and oxygen delivery to vital organs. To recognize sudden cardiac arrest, look for the following signs:
If you suspect sudden cardiac arrest, immediately ask someone nearby to call 911 or your local emergency response number. If you’re alone, call for help yourself before beginning CPR. In addition, request for an Automated External Defibrillator (AED) if available.
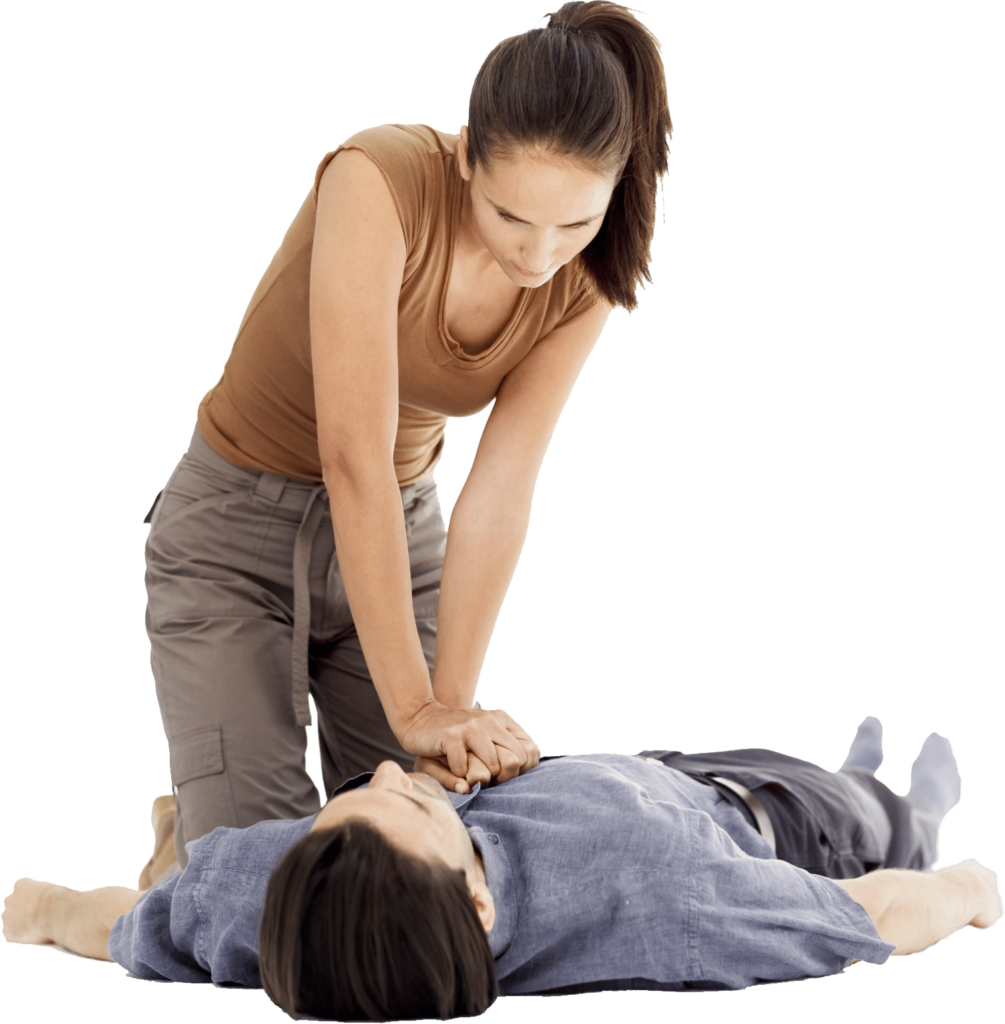
3. Delivering High-Quality Chest Compressions
Once you’ve ensured your safety, recognized sudden cardiac arrest, and activated the emergency response system, initiate CPR by performing chest compressions. Follow these steps for effective chest compressions:
4. Administering Rescue Breaths
After delivering 30 chest compressions, give two rescue breaths by following these steps:
Return to chest compressions after giving two rescue breaths, and continue the cycle of 30 compressions and two breaths until help arrives or the victim regains consciousness.
5. Utilizing an Automated External Defibrillator (AED)
If an AED is available, turn it on and follow the voice prompts, performing CPR while preparing the device if possible. Attach the self-adhesive pads to the victim’s bare chest as displayed on the illustrations, ensuring there’s no water, sweat, or debris on the skin. Stop CPR while the AED analyzes the heart rhythm, and follow its instructions for either resuming CPR or administering a shock.
The ability to perform CPR effectively is a critical lifesaving skill that can greatly impact the chances of survival for those experiencing sudden cardiac arrest. By mastering the basics of CPR through quality training and hands-on practice, you can make a profound difference in emergencies and take an active role in safeguarding your loved ones and community.
Enroll in our AHA CPA classes in Dallas at Rapid CPR Dallas and gain the essential knowledge, skills, and confidence required to save lives and make a difference when it matters the most.